Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
See the following -
Open Source Penn Software Helps to Identify Course of Cancer Metastasis, Tumor "Evolution"
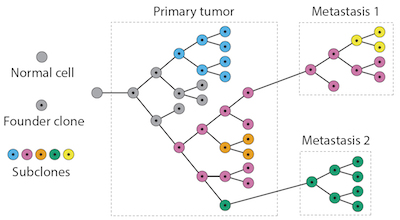 Researchers have come to realize that cancer is a disease driven by the same “survival of the fitter” forces that Darwin proposed drove the evolution of life on Earth. In the case of tumors, however, individual cells are constantly evolving as a tumor’s stage advances. Mobile cancer cells causing metastasis are a deadly outcome of this process. Tumors also differ among patients with the same type of cancer, so how is a physician able to prescribe a tailored regimen for the patient? To start to address this conundrum, an interdisciplinary team from the Perelman School of Medicine and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania developed Canopy...
Researchers have come to realize that cancer is a disease driven by the same “survival of the fitter” forces that Darwin proposed drove the evolution of life on Earth. In the case of tumors, however, individual cells are constantly evolving as a tumor’s stage advances. Mobile cancer cells causing metastasis are a deadly outcome of this process. Tumors also differ among patients with the same type of cancer, so how is a physician able to prescribe a tailored regimen for the patient? To start to address this conundrum, an interdisciplinary team from the Perelman School of Medicine and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania developed Canopy...
- Login to post comments
Scientists Develop ‘Lab on a Chip’ That Costs 1 Cent to Make
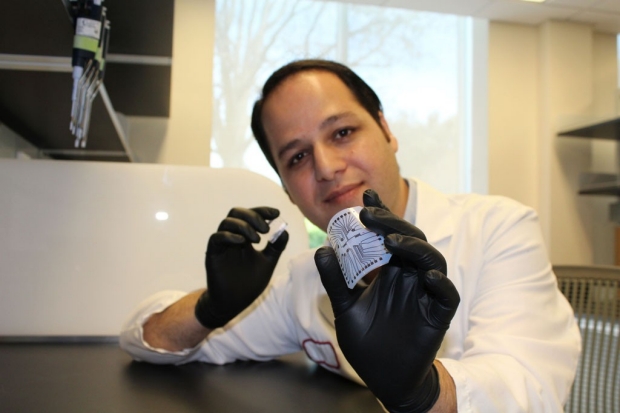 Researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have developed a way to produce a cheap and reusable diagnostic “lab on a chip” with the help of an ordinary inkjet printer. At a production cost of as little as 1 cent per chip, the new technology could usher in a medical diagnostics revolution like the kind brought on by low-cost genome sequencing, said Ron Davis, PhD, professor of biochemistry and of genetics and director of the Stanford Genome Technology Center...
Researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have developed a way to produce a cheap and reusable diagnostic “lab on a chip” with the help of an ordinary inkjet printer. At a production cost of as little as 1 cent per chip, the new technology could usher in a medical diagnostics revolution like the kind brought on by low-cost genome sequencing, said Ron Davis, PhD, professor of biochemistry and of genetics and director of the Stanford Genome Technology Center...
- Login to post comments
The Growing Field of Ecotherapy
The first time J. Phoenix Smith told me that soil has healing properties that can help thwart depression, I just nodded slowly. Smith is an ecotherapist, a practitioner of nature-based exercises intended to address both mental and physical health. Which means she recommends certain therapies that trigger in me, as a medical doctor, more skepticism than serenity: Listen to birdsong, in your headphones if necessary. Start a garden, and think of the seeds’ growth as a metaphor for life transitions. Find a spot in a park and sit there for 20 minutes every week, without checking your phone, noting week-to-week and seasonal changes in a journal...
- Login to post comments
Wearable Sweat Sensor Can Diagnose Cystic Fibrosis, Study Finds
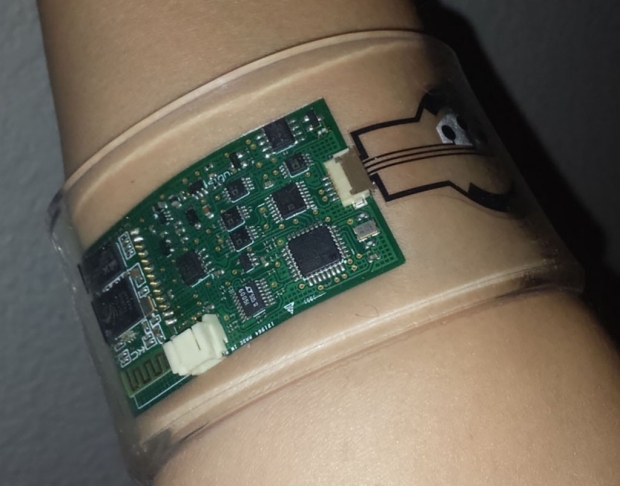 A wristband-type wearable sweat sensor could transform diagnostics and drug evaluation for cystic fibrosis, diabetes and other diseases. The sensor collects sweat, measures its molecular constituents and then electronically transmits the results for analysis and diagnostics, according to a study led by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine, in collaboration with the University of California-Berkeley. Unlike old-fashioned sweat collectors, the new device does not require patients to sit still for a long time while sweat accumulates in the collectors...
A wristband-type wearable sweat sensor could transform diagnostics and drug evaluation for cystic fibrosis, diabetes and other diseases. The sensor collects sweat, measures its molecular constituents and then electronically transmits the results for analysis and diagnostics, according to a study led by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine, in collaboration with the University of California-Berkeley. Unlike old-fashioned sweat collectors, the new device does not require patients to sit still for a long time while sweat accumulates in the collectors...
- Login to post comments