gene sequencing
See the following -
A Deadly Superbug Appears to Be Invading America's Hospitals
A dangerous type of superbug has more tricks up its sleeves than we may be giving it credit for, a recent study suggests. The researchers found that this class of bacteria, CREs — that's short for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae — has more ways to evade antibiotics than have been currently identified, and that these bugs share their tricks readily across the families of bacteria that make up this grouping...
- Login to post comments
Maintaining Health Data Privacy in Precision Medicine Push
As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve and put PHI at risk, precision medicine guidelines need to be updated to account for new health data privacy threats, according to a recent opinion piece published in the Oxford University Press. The Johns Hopkins Hospital and Health System Senior Counsel Jennifer Kulynych, JD, PhD explained that data re-identification methods are not foolproof, and it can be difficult to determine exactly how individuals’ genomes are being used...
- Login to post comments
Open Source Penn Software Helps to Identify Course of Cancer Metastasis, Tumor "Evolution"
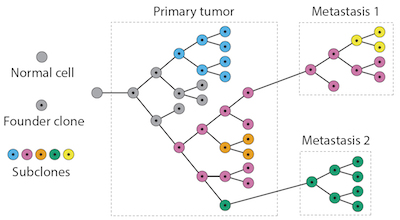 Researchers have come to realize that cancer is a disease driven by the same “survival of the fitter” forces that Darwin proposed drove the evolution of life on Earth. In the case of tumors, however, individual cells are constantly evolving as a tumor’s stage advances. Mobile cancer cells causing metastasis are a deadly outcome of this process. Tumors also differ among patients with the same type of cancer, so how is a physician able to prescribe a tailored regimen for the patient? To start to address this conundrum, an interdisciplinary team from the Perelman School of Medicine and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania developed Canopy...
Researchers have come to realize that cancer is a disease driven by the same “survival of the fitter” forces that Darwin proposed drove the evolution of life on Earth. In the case of tumors, however, individual cells are constantly evolving as a tumor’s stage advances. Mobile cancer cells causing metastasis are a deadly outcome of this process. Tumors also differ among patients with the same type of cancer, so how is a physician able to prescribe a tailored regimen for the patient? To start to address this conundrum, an interdisciplinary team from the Perelman School of Medicine and the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania developed Canopy...
- Login to post comments
Open Source Web App Helps Researchers Explore Cancer Genetics
 Brown University computer scientists have developed a new interactive tool to help researchers and clinicians explore the genetic underpinnings of cancer. The tool — dubbed MAGI, for Mutation Annotation and Genome Interpretation — is an open-source web application that enables users to search, visualize, and annotate large public cancer genetics datasets, including data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project. “The main motivation for MAGI has been to reduce the computational burden required for researchers or doctors to explore and annotate cancer genomics data,” said Max Leiserson, a Ph.D. student at Brown who led the development of the tool.
Brown University computer scientists have developed a new interactive tool to help researchers and clinicians explore the genetic underpinnings of cancer. The tool — dubbed MAGI, for Mutation Annotation and Genome Interpretation — is an open-source web application that enables users to search, visualize, and annotate large public cancer genetics datasets, including data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project. “The main motivation for MAGI has been to reduce the computational burden required for researchers or doctors to explore and annotate cancer genomics data,” said Max Leiserson, a Ph.D. student at Brown who led the development of the tool.
- Login to post comments